Complex Numbers
Complex numbers are fundamental to signal processing. They provide an elegant way to represent and manipulate sinusoidal signals, analyze frequency content, and describe system behavior.
The Imaginary Unit
Definition
The imaginary unit
Properties
Powers of
Python Implementation
import numpy as np
# In Python/NumPy, the imaginary unit is 1j
j = 1j
print(f"j = {j}")
print(f"j² = {j**2}")
print(f"j³ = {j**3}")
print(f"j⁴ = {j**4}")Rectangular Form
Definition
A complex number
where:
is the real part is the imaginary part
The Complex Plane
Complex numbers are visualized on the complex plane (Argand diagram), where the horizontal axis represents the real part and the vertical axis represents the imaginary part.
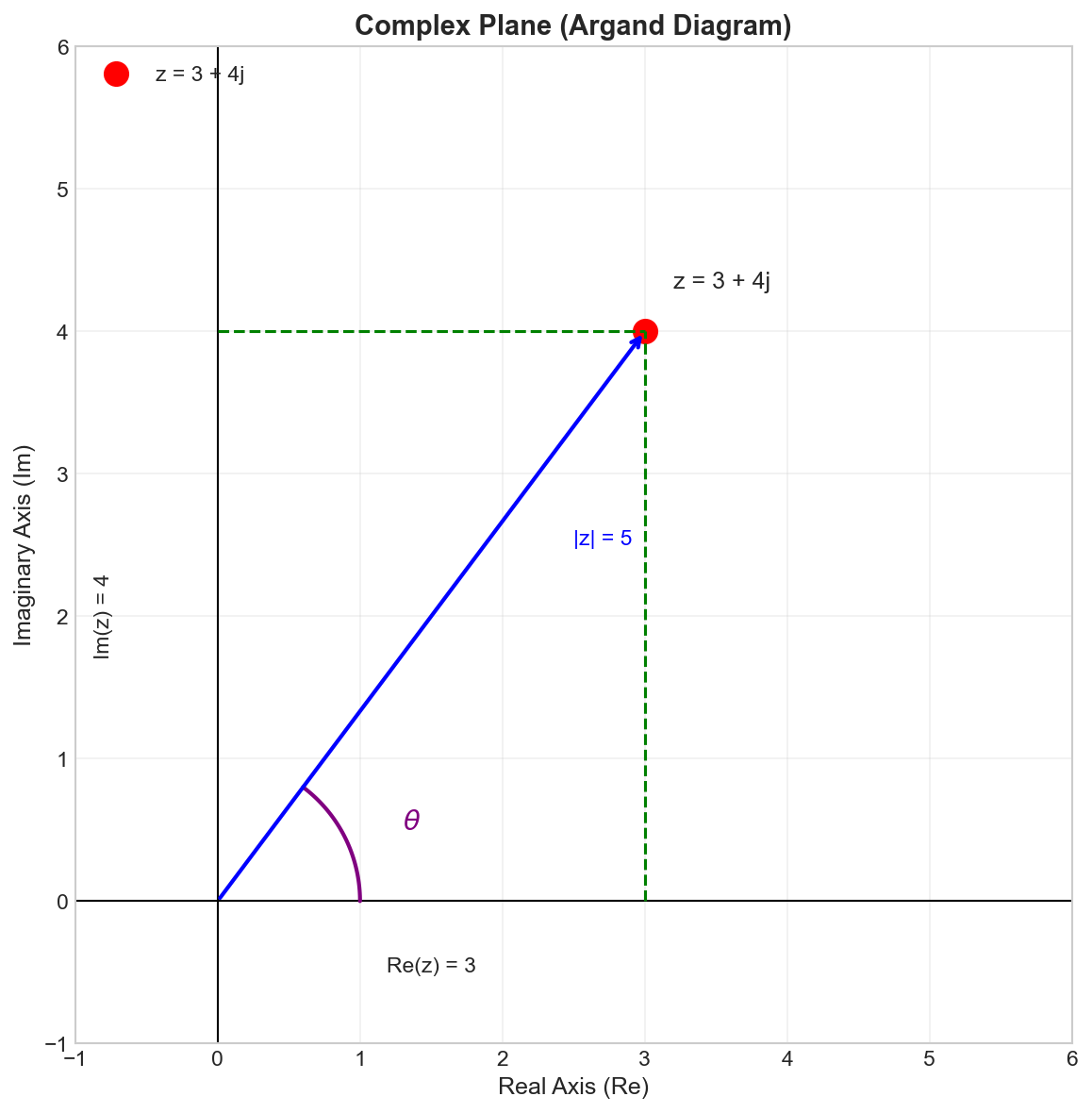
Properties
Equality: Two complex numbers are equal if and only if their real and imaginary parts are equal:
Complex Conjugate: The complex conjugate of
Python Implementation
import numpy as np
# Define a complex number
z = 3 + 4j
# Extract real and imaginary parts
print(f"z = {z}")
print(f"Real part: Re(z) = {z.real}")
print(f"Imaginary part: Im(z) = {z.imag}")
print(f"Complex conjugate: z* = {np.conj(z)}")
# Verify: z * z* = |z|²
print(f"z × z* = {z * np.conj(z)} = |z|² = {abs(z)**2}")Polar Form
Definition
A complex number can also be expressed in polar form:
where:
is the magnitude (or modulus) is the phase (or argument)
Properties
Conversion from Rectangular:
(Note: Use atan2(y, x) in code to handle all quadrants correctly)
Conversion to Rectangular:
Python Implementation
import numpy as np
z = 3 + 4j
# Magnitude and phase
r = np.abs(z)
theta = np.angle(z) # in radians
print(f"z = {z}")
print(f"Magnitude: |z| = {r}")
print(f"Phase: θ = {theta:.4f} rad = {np.degrees(theta):.2f}°")
# Convert back to rectangular
x = r * np.cos(theta)
y = r * np.sin(theta)
z_reconstructed = x + 1j * y
print(f"Reconstructed: z = {z_reconstructed}")Exponential Form and Euler's Formula
Euler's Formula
Euler's formula is one of the most important results in mathematics:
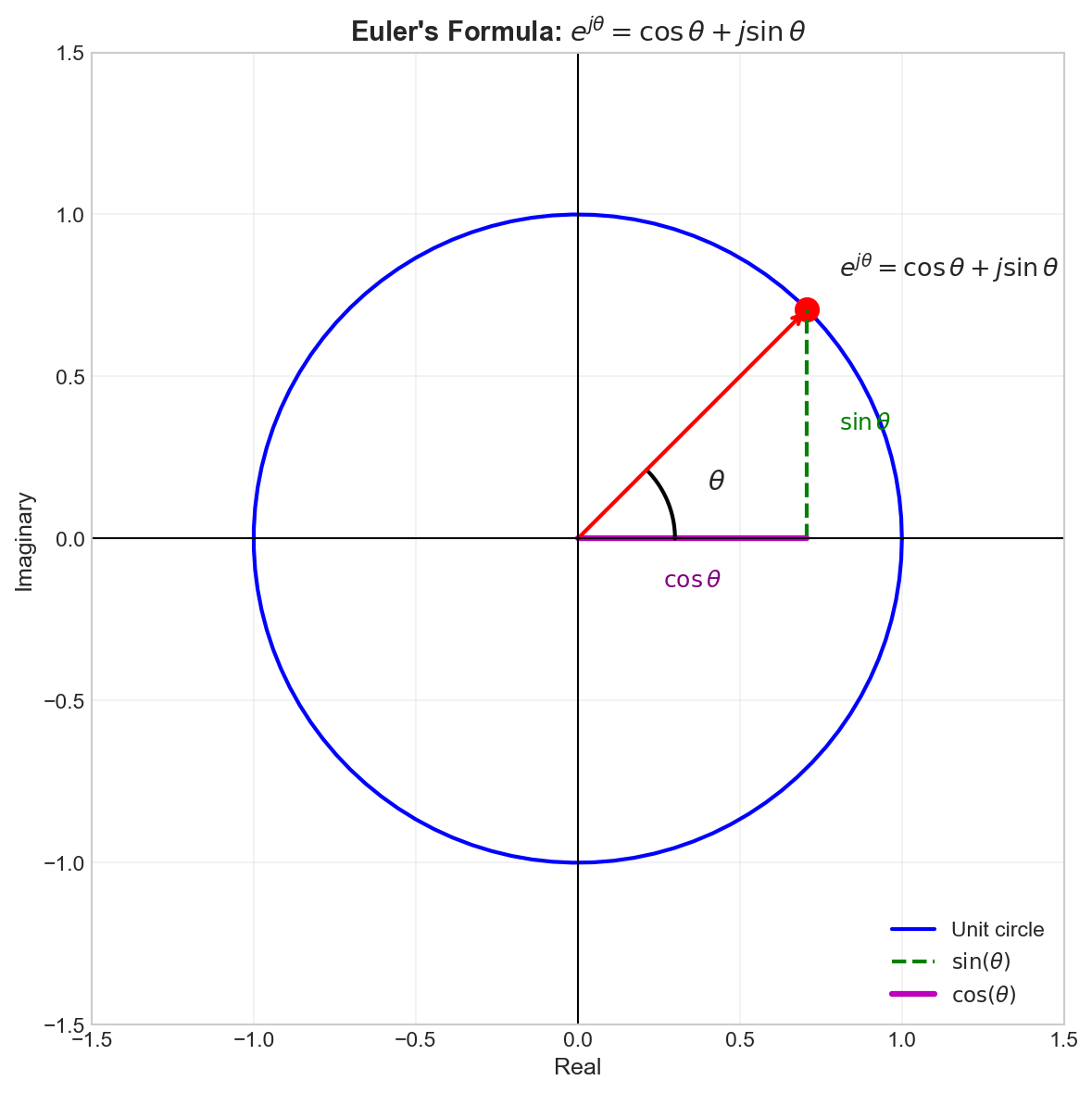
Properties
From Euler's formula, we can derive:
Cosine and Sine as Exponentials:
Exponential Form of Complex Numbers:
This combines magnitude and phase into a compact notation.
Python Implementation
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Verify Euler's formula
theta = np.pi / 4 # 45 degrees
euler_lhs = np.exp(1j * theta)
euler_rhs = np.cos(theta) + 1j * np.sin(theta)
print(f"e^(jθ) = {euler_lhs}")
print(f"cos(θ) + j·sin(θ) = {euler_rhs}")
print(f"Difference: {abs(euler_lhs - euler_rhs):.2e}")
# Express z = 3 + 4j in exponential form
z = 3 + 4j
r = np.abs(z)
theta = np.angle(z)
z_exp = r * np.exp(1j * theta)
print(f"\nz = {z}")
print(f"z = {r:.4f} × e^(j × {theta:.4f})")
print(f"Verification: {z_exp}")Complex Arithmetic
Addition and Subtraction
Add/subtract real and imaginary parts separately:
Multiplication
In rectangular form:
In polar/exponential form (more elegant):
Magnitudes multiply, phases add.
Division
In rectangular form:
In polar/exponential form:
Magnitudes divide, phases subtract.
Python Implementation
import numpy as np
z1 = 3 + 4j
z2 = 1 + 2j
# Basic operations
print(f"z1 = {z1}")
print(f"z2 = {z2}")
print(f"z1 + z2 = {z1 + z2}")
print(f"z1 - z2 = {z1 - z2}")
print(f"z1 × z2 = {z1 * z2}")
print(f"z1 / z2 = {z1 / z2}")
# Verify multiplication rule: |z1 × z2| = |z1| × |z2|
print(f"\n|z1 × z2| = {np.abs(z1 * z2):.4f}")
print(f"|z1| × |z2| = {np.abs(z1) * np.abs(z2):.4f}")
# Verify: angle(z1 × z2) = angle(z1) + angle(z2)
print(f"\nangle(z1 × z2) = {np.angle(z1 * z2):.4f}")
print(f"angle(z1) + angle(z2) = {np.angle(z1) + np.angle(z2):.4f}")Complex Exponentials and Rotation
The Unit Circle
The complex exponential
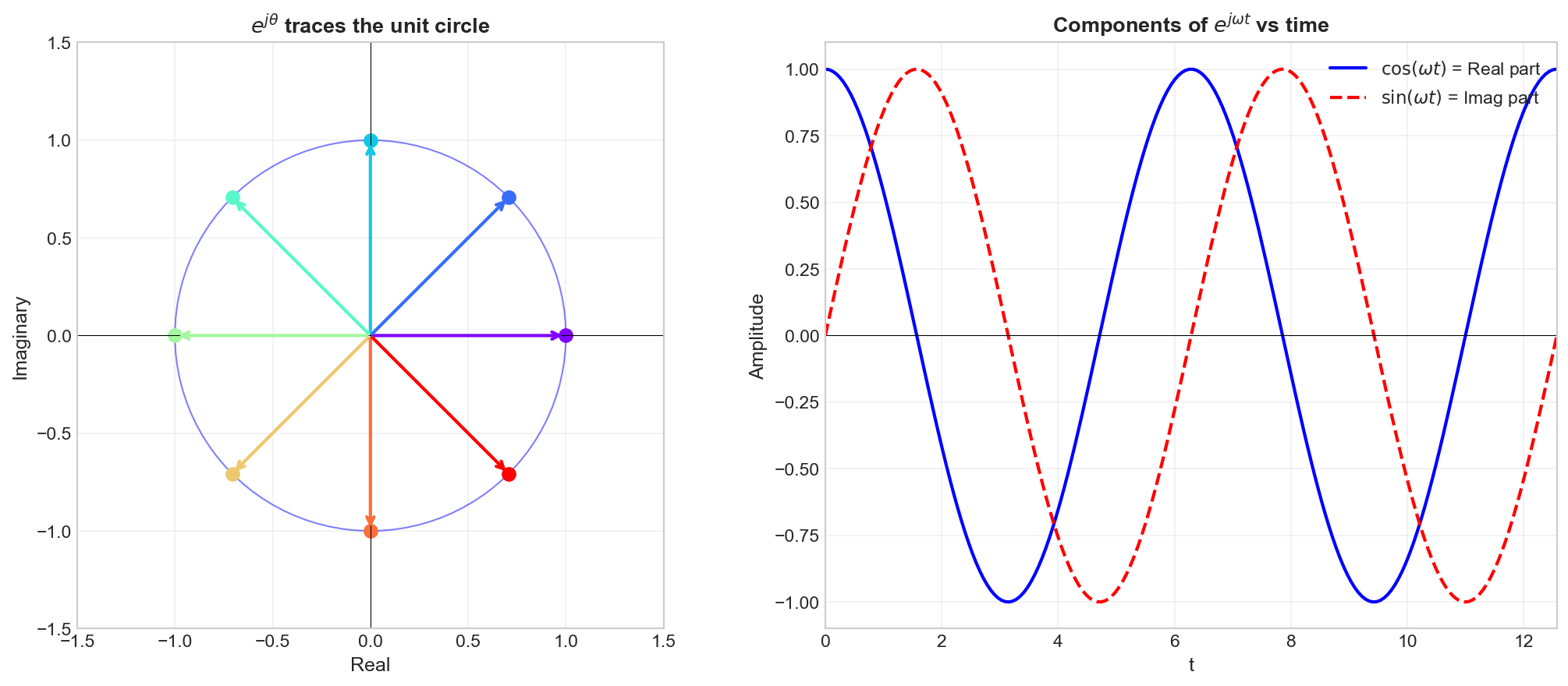
Properties
Rotating Phasor:
Periodicity:
De Moivre's Theorem:
Python Implementation
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# e^(jωt) traces the unit circle
t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
omega = 1
z = np.exp(1j * omega * t)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
# Left: trajectory in complex plane
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(np.real(z), np.imag(z), 'b-', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(1, 0, 'ro', markersize=10, label='Start (t=0)')
plt.xlabel('Real')
plt.ylabel('Imaginary')
plt.title(r'$e^{j\omega t}$ on Complex Plane')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
# Right: real and imaginary parts vs time
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(t, np.real(z), 'b-', linewidth=2, label=r'$\cos(\omega t)$')
plt.plot(t, np.imag(z), 'r--', linewidth=2, label=r'$\sin(\omega t)$')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.title(r'Components of $e^{j\omega t}$')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Key Formulas
| Formula | Expression |
|---|---|
| Euler's formula | |
| Magnitude | |
| Phase | |
| Conjugate | |
| Cosine | |
| Sine |