Continuous-Time Signals
Welcome to the continuous-time signals section of this course.
What is a Signal?
A signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. In its most general form, a signal is a mapping from an independent variable (often time or space) to a dependent variable that represents some physical quantity.
Definition: A signal is a function
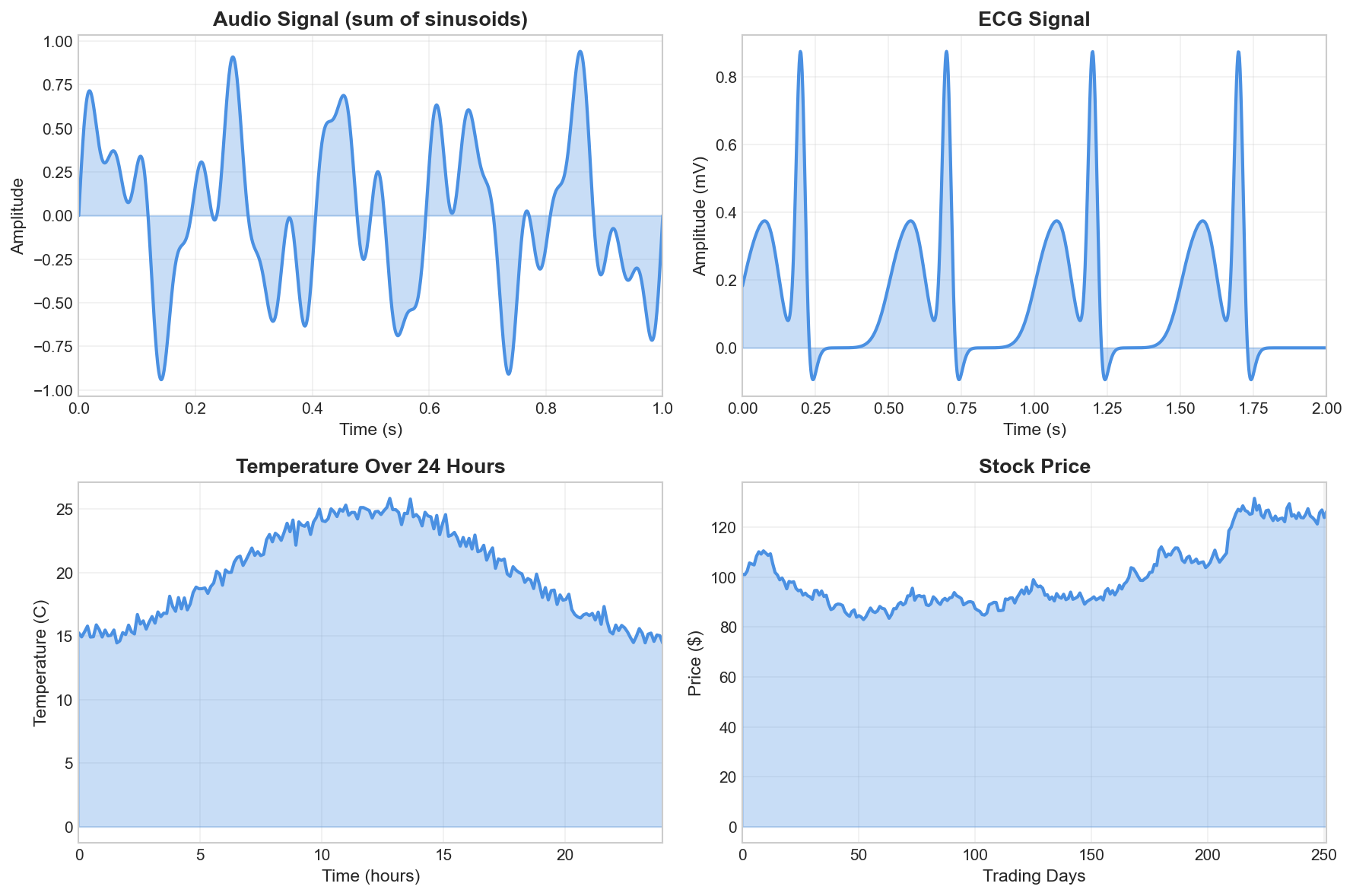
In this course, we focus on one-dimensional signals where the independent variable is time. Such signals are ubiquitous in engineering and science:
- Audio signals: sound pressure variations over time
- Biomedical signals: ECG (heart activity), EEG (brain activity)
- Communication signals: voltage or current in electronic circuits
- Financial signals: stock prices, economic indicators
- Environmental signals: temperature, pressure, seismic activity
Signal Classification
Signals can be classified based on different characteristics.
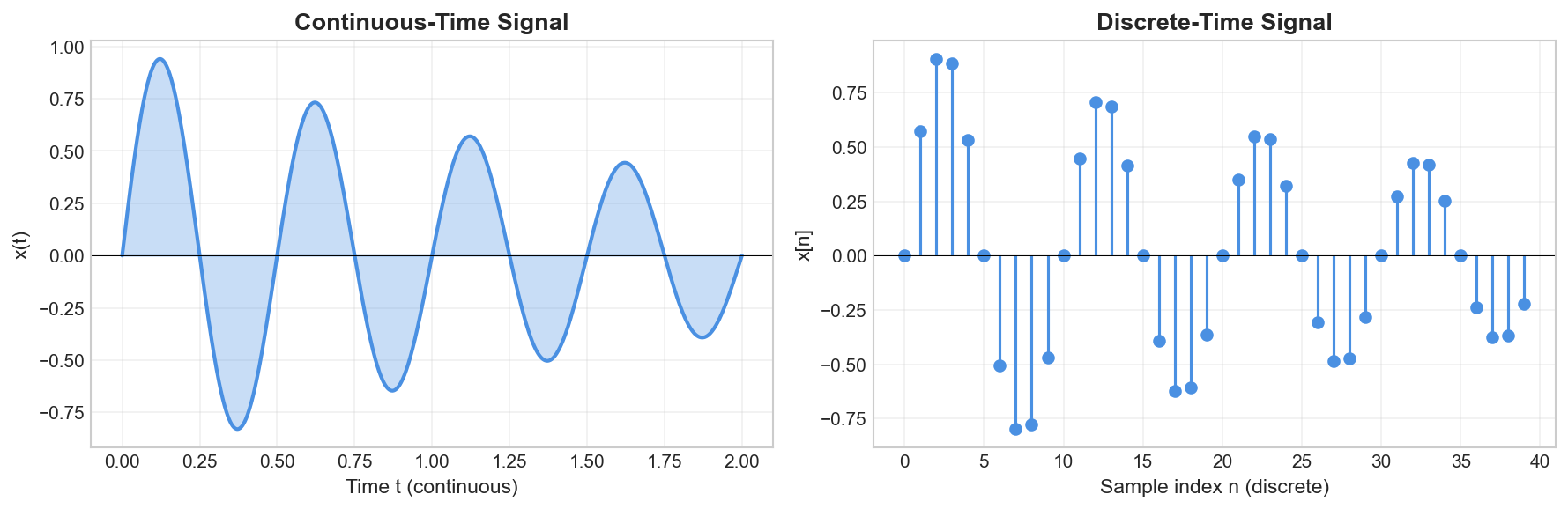
Continuous-Time vs Discrete-Time Signals
Continuous-time signals are defined for all values of time
Discrete-time signals are defined only at discrete instants, typically integer multiples of a sampling period. We denote them as
Deterministic vs Random Signals
- Deterministic signals: can be described by an explicit mathematical expression
- Random (stochastic) signals: cannot be predicted exactly; described statistically using a probability density function.
Energy and Power Signals
The energy of a continuous-time signal is:
The average power is:
- Energy signal:
(and ) - Power signal:
(and )
What is a System ?
A system is a mathematical model that transforms an input signal into an output signal. Systems can be classified based on the number of inputs and outputs:
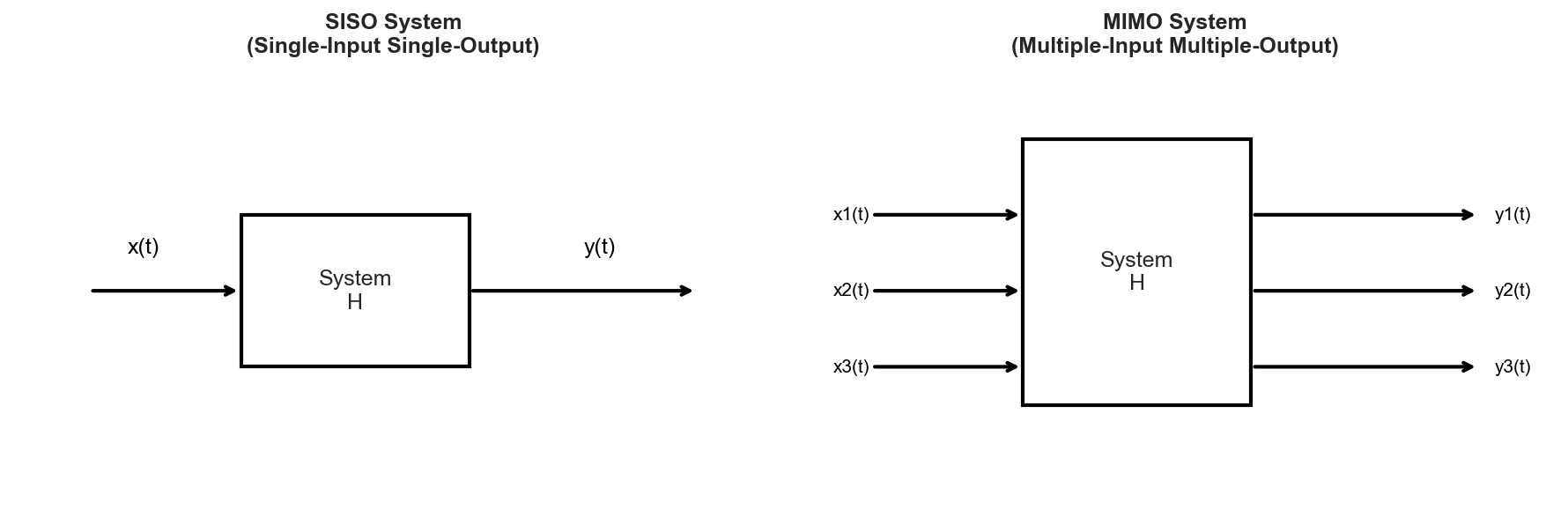
SISO Systems
A Single-Input Single-Output (SISO) system has one input signal
MIMO Systems
A Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) system has multiple inputs
Objectives
This module covers the fundamental concepts of analog signal processing:
- Representation and classification of continuous-time signals
- Analysis of SISO Linear Time-Invariant (LTI) systems
- Fourier series decomposition of periodic signals
- Fourier transform for aperiodic signals
- Laplace transform and its applications
Prerequisites
- Calculus (integrals, derivatives)
- Complex numbers
- Basic linear algebra
Notation
A continuous-time signal is denoted