Chapter 1: Elementary Signals
This chapter presents the elementary signals used in signal processing. These fundamental building blocks form the basis for analyzing more complex signals and systems.
Dirac Delta Function
Definition
The Dirac delta function
While not a function in the classical sense,
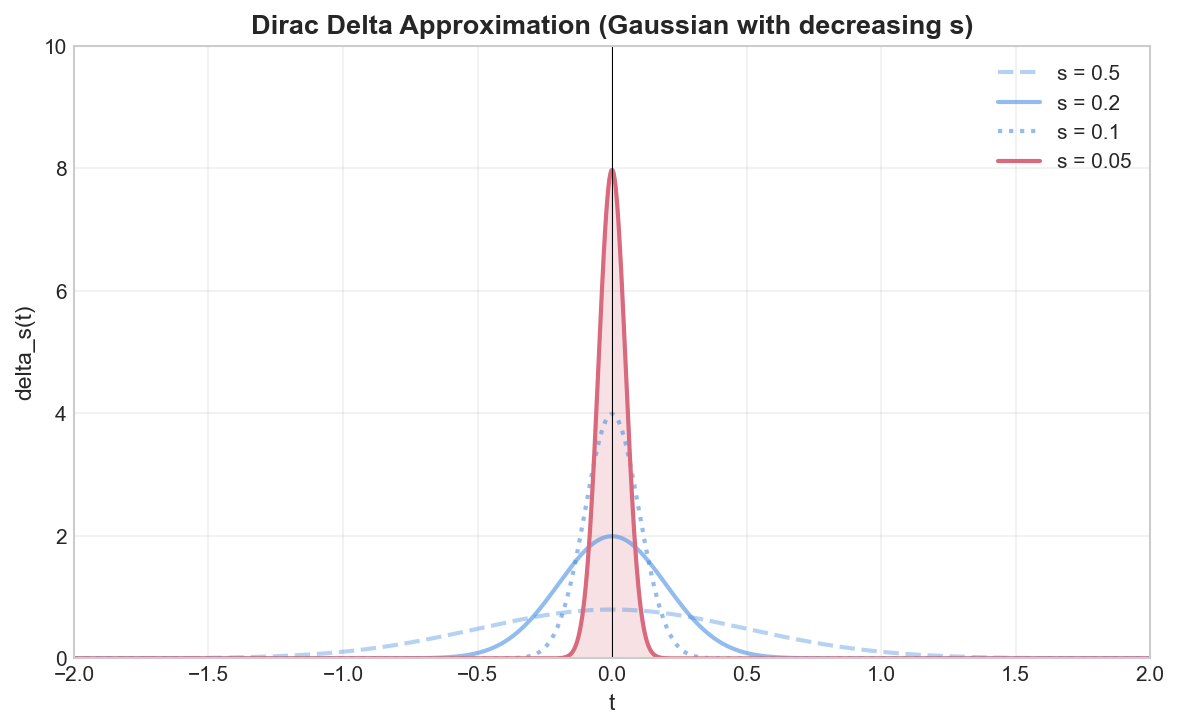
Properties
Sifting Property: For any function
Scaling Property:
Derivative Property:
Unit Step Function
Definition
The unit step function (Heaviside function) is defined as:
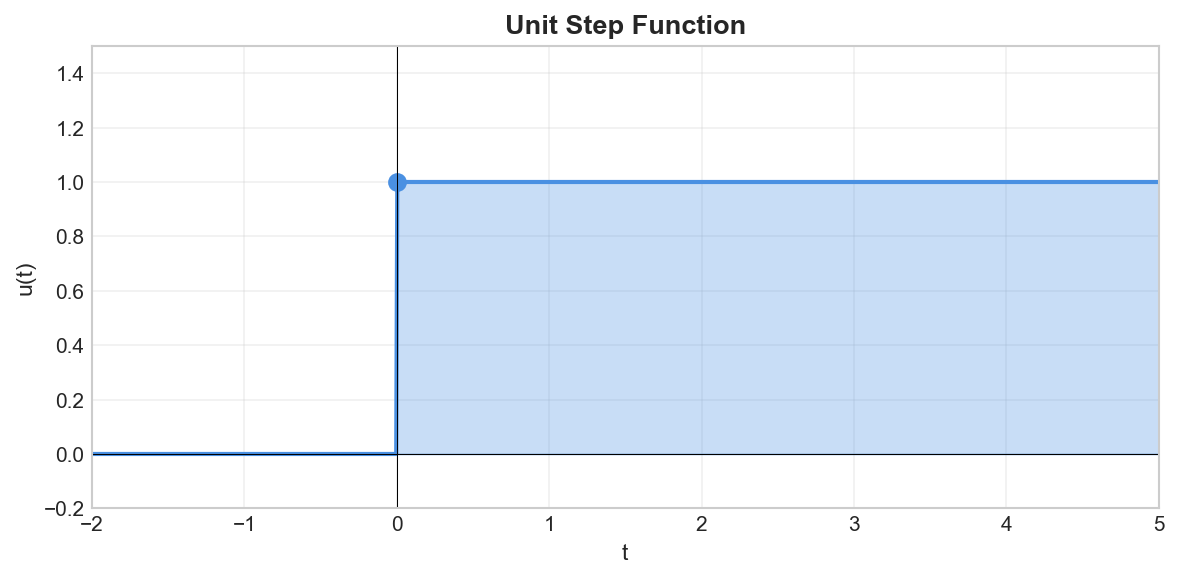
Properties
Relationship with Dirac Delta:
Windowing: The unit step can be used to "turn on" a signal at
Shifted Step: A step delayed by
Unit Ramp Function
Definition
The unit ramp function is defined as:
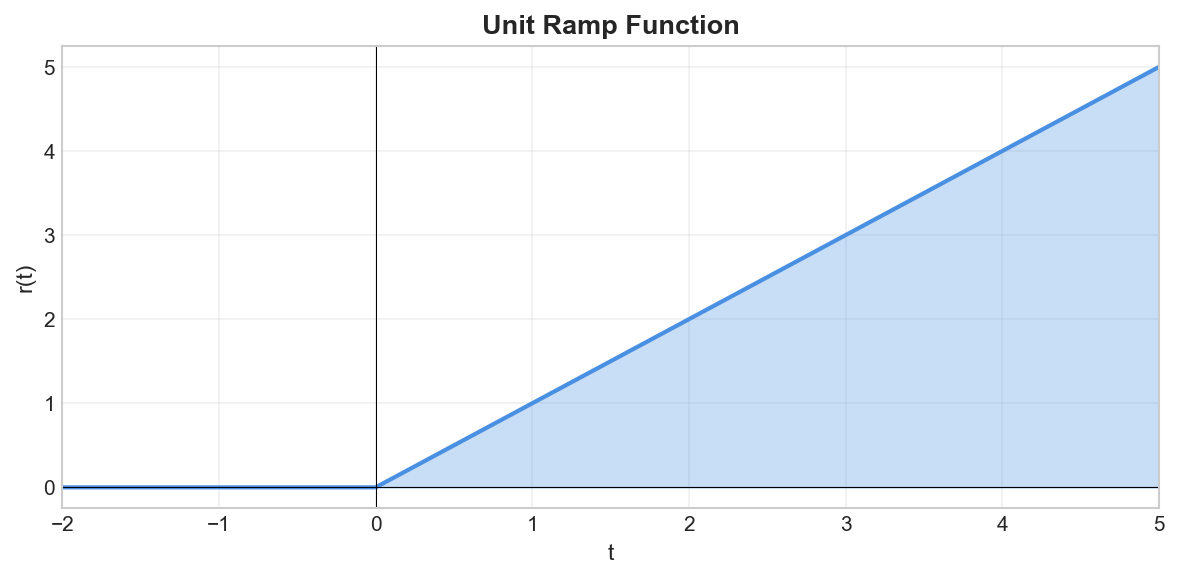
Properties
Relationship with Unit Step:
Relationship with Dirac Delta:
Complex Exponential
Definition
The complex exponential is defined as:
where:
is the complex frequency is the amplitude is the damping factor (attenuation) is the angular frequency (rad/s)
Using Euler's formula
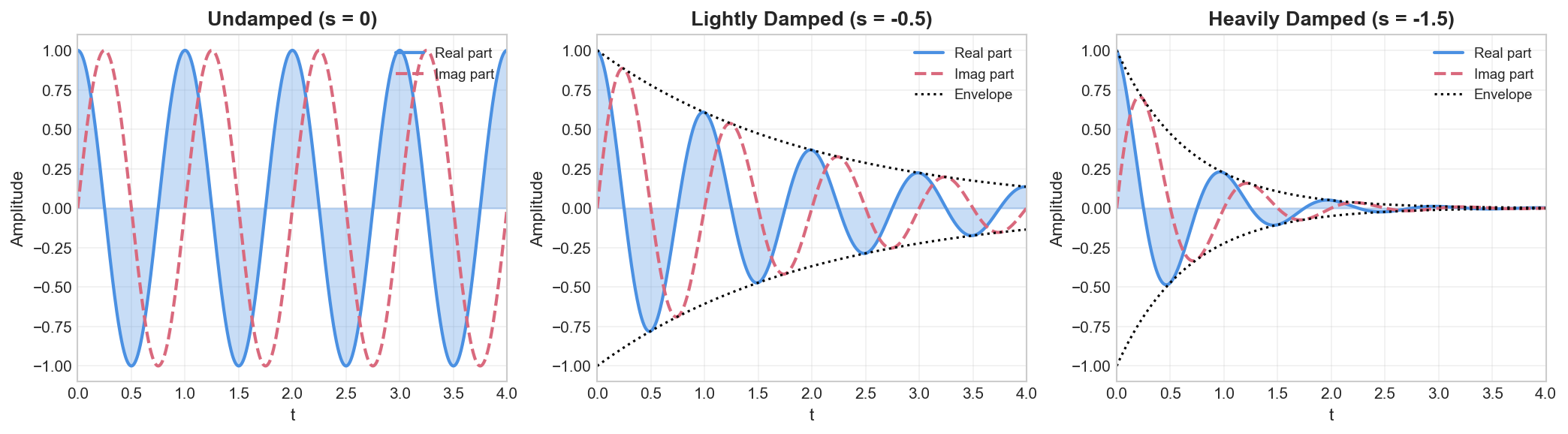
Properties
Euler's Formula:
Behavior based on
: undamped oscillation (constant amplitude) : damped oscillation (decaying amplitude) : growing oscillation (unstable)
Eigenfunction Property: Complex exponentials are eigenfunctions of LTI systems:
Periodicity: When
Sinusoidal Signal
Definition
A sinusoidal signal is defined as:
where:
: amplitude (peak value) : angular frequency (rad/s) : frequency (Hz) : period (s) : initial phase (rad)
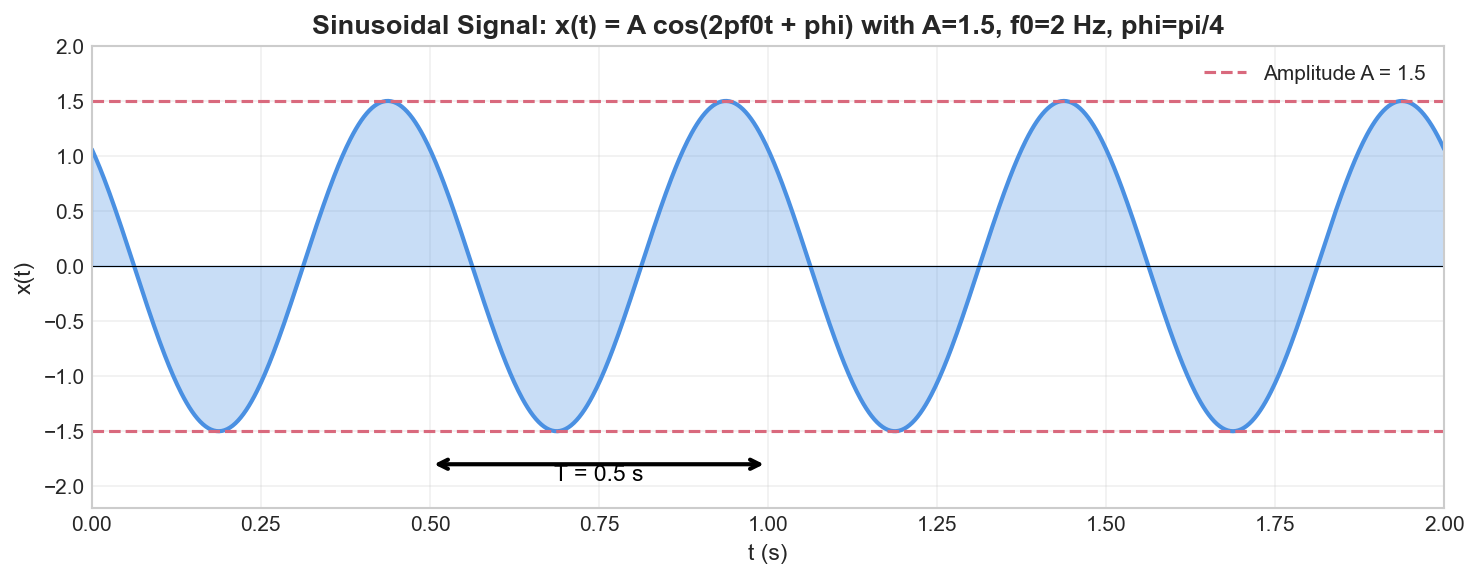
Properties
Periodicity:
Relation to Complex Exponentials:
Power: A sinusoid is a power signal with average power:
Phase Shift: A time delay
Rectangular Pulse
Definition
The rectangular pulse (gate function) of width
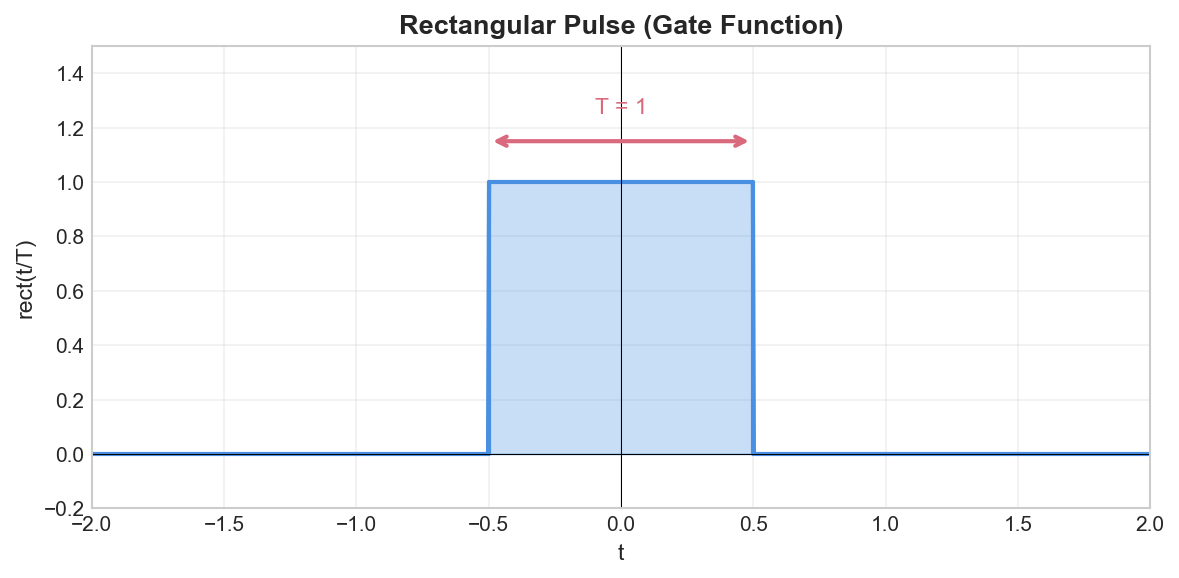
Properties
Relation to Unit Steps:
Area:
Energy:
Fourier Transform: The Fourier transform of a rectangular pulse is a sinc function:
Sinc Function
Definition
The normalized sinc function is defined as:
with
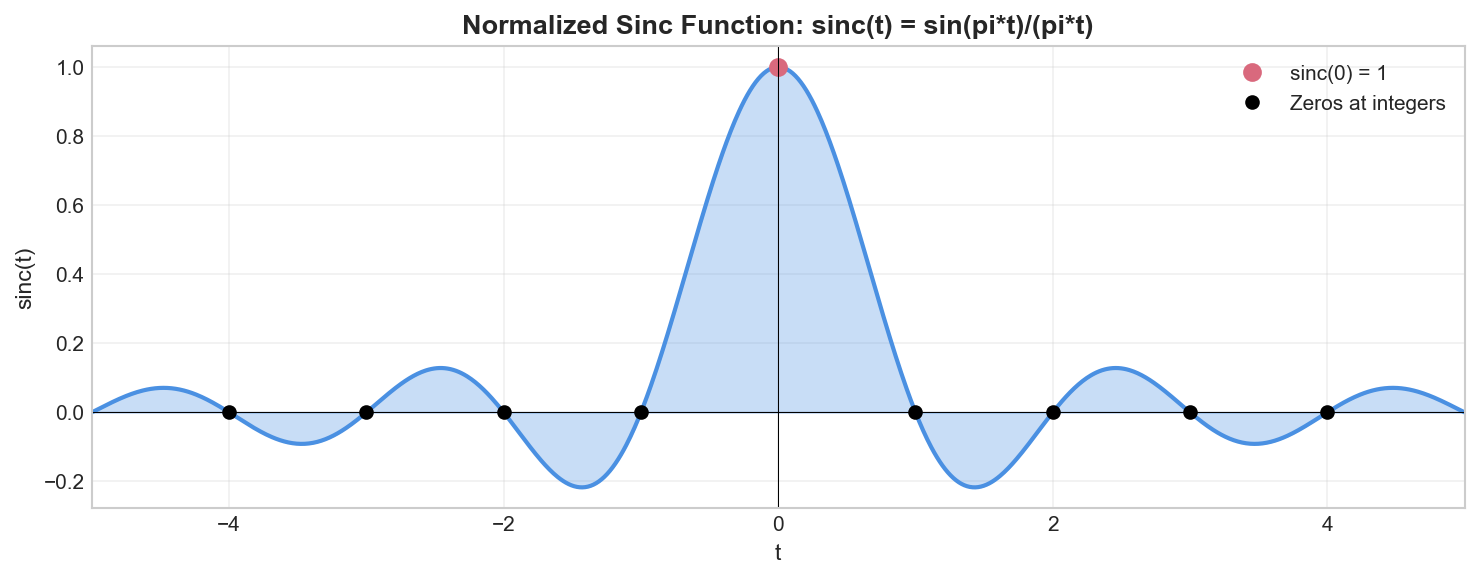
Properties
Zeros:
Normalization:
Fourier Transform Pair: The sinc and rect functions are Fourier transform pairs:
Ideal Lowpass Filter: The sinc function is the impulse response of an ideal lowpass filter.
Interpolation: The sinc function appears in the ideal reconstruction formula (Whittaker-Shannon interpolation).
Gaussian Pulse
Definition
The Gaussian pulse is defined as:
More generally, with parameter
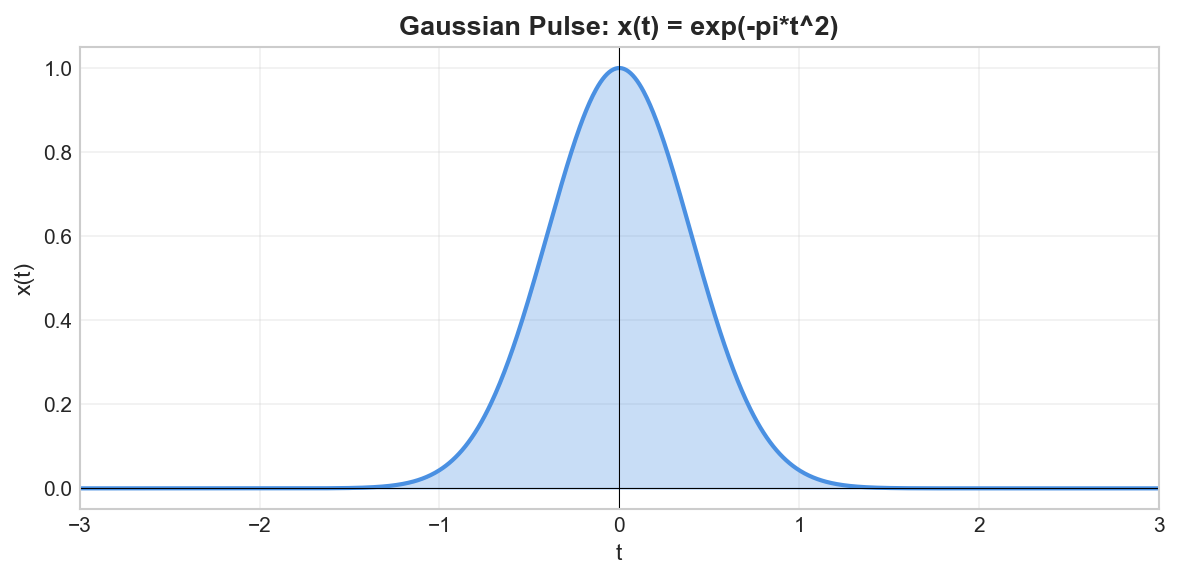
Properties
Self-Fourier Transform: The Gaussian is its own Fourier transform (with appropriate normalization):
Uncertainty Principle: The Gaussian achieves the lower bound of the time-frequency uncertainty principle:
Energy:
Smoothness: The Gaussian is infinitely differentiable and has no discontinuities.
Summary
| Signal | Definition | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Dirac delta | Unit impulse at | Sifting property |
| Unit step | 1 for | |
| Unit ramp | ||
| Complex exponential | Eigenfunction of LTI systems | |
| Sinusoid | Periodic, period | |
| Rectangular pulse | 1 for | FT is sinc |
| Sinc | FT is rect | |
| Gaussian | Self-Fourier transform |